Are you ready to unlock the power of forex trading indicators and take control of your investments? In the dynamic world of finance, understanding the significance of indicators is your key to success.
Meet MACD, the Moving Average Convergence Divergence indicator, your ultimate ally in navigating the markets. In this blog, we’ll demystify MACD, providing you with the tools and knowledge needed to master it.
From deciphering its signals to utilizing divergence and convergence, we’ll guide you through every aspect. Get ready to elevate your trading game, as we embark on a journey to maximize your profit potential with MACD.
What is MACD?
MACD stands for Moving Average Convergence Divergence. It is a powerful and widely-used technical indicator in forex trading.
At its core, MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator, meaning it helps traders identify the direction and strength of a currency’s price trend. Here’s a breakdown of its key components:
MACD Line (Blue Line):
- The MACD line is calculated by subtracting the 26-period Exponential Moving Average (EMA) from the 12-period EMA.
- The result is a line that represents the short-term momentum of the price movement.
- When the MACD line moves above the Signal line, it indicates bullish momentum.
- Conversely, when it moves below the Signal line, it signals bearish momentum.
Signal Line (Orange Line):
- The Signal line is a 9-period Exponential Moving Average (EMA) of the MACD line.
- It helps smooth out the MACD line, making it easier to identify trends and potential trading signals.
- Crossovers between the MACD line and the Signal line generate buy (bullish) or sell (bearish) signals.
- When the MACD line crosses above the Signal line, it suggests a potential buying opportunity.
- Conversely, when the MACD line crosses below the Signal line, it suggests a potential selling opportunity.
MACD is a versatile indicator that traders use to assess the strength and direction of a trend. It does this by comparing two EMAs (the 12-period and 26-period) and generates trading signals through the MACD line’s relationship with the Signal line.
It’s a valuable tool for both short-term and long-term traders, helping them make informed decisions in the forex market.
How MACD Works?
MACD works by calculating the difference between two exponential moving averages to gauge momentum and generates trading signals through crossovers and histogram analysis.
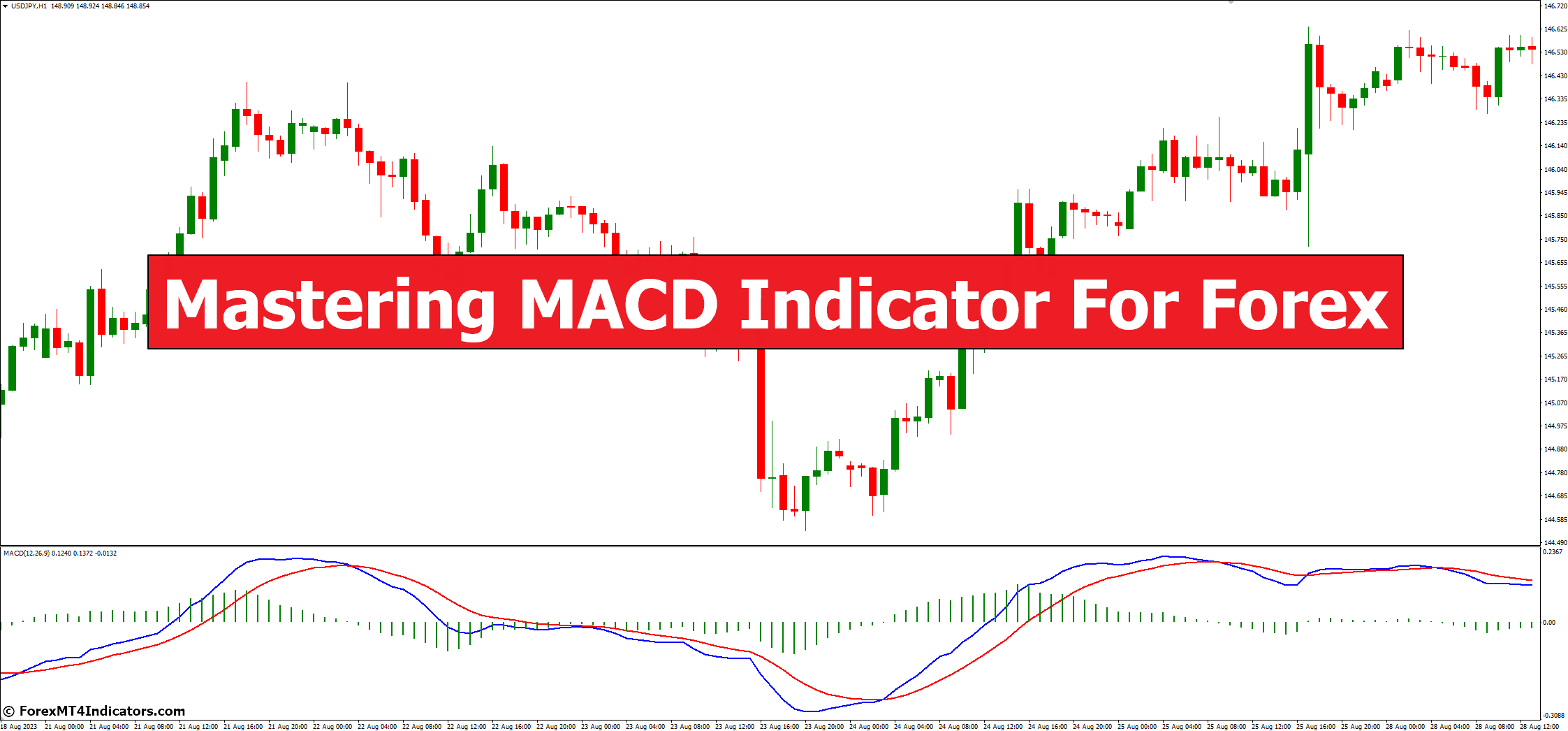
In the chart below, you can observe how the two Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs) overlaid on the price chart align.
Calculation Using Moving Averages:
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) is calculated by subtracting the 26-period Exponential Moving Average (EMA) from the 12-period EMA. This calculation results in the MACD line.
- The MACD line represents the short-term momentum of the price movement. The 12-period EMA reacts more quickly to recent price changes, while the 26-period EMA provides a slightly slower moving average.
Interpreting MACD Line and Signal Line Crossovers:
- The MACD line is the blue line on the MACD chart, and the Signal line is the orange line.
- When the MACD line crosses above the Signal line, it generates a bullish signal. This crossover suggests that short-term price momentum is increasing relative to the longer-term momentum, potentially signaling an uptrend.
- Conversely, when the MACD line crosses below the Signal line, it produces a bearish signal. This crossover implies that short-term price momentum is weakening compared to the longer-term momentum, potentially indicating a downtrend.
- Traders often use these crossovers to time their buy and sell decisions.
Significance of the Histogram:
- The histogram on the MACD chart is formed by the vertical bars that represent the difference between the MACD line and the Signal line.
- Histogram bars above the zero line indicate that the MACD line is above the Signal line, signaling bullish momentum. The taller the bars, the stronger the momentum.
- Histogram bars below the zero line indicate that the MACD line is below the Signal line, signaling bearish momentum. Again, the height of the bars reflects the strength of the bearish momentum.
- Zero-line crossovers of the histogram indicate changes in the overall trend direction. When the histogram crosses from negative to positive, it suggests a potential shift from a bearish to a bullish trend, and vice versa.
MACD helps traders understand the relationship between short-term and long-term moving averages, providing insights into a momentum and potential trend reversals.
The MACD line and Signal line crossovers are used to generate buy and sell signals, while the histogram provides a visual representation of the difference in momentum between these lines.
Effective interpretation of MACD components can assist traders in making informed decisions in the forex market.
Using MACD For Forex Trading Style
In this guide, we’ll break down the practical use of MACD indicator consists with clear examples, providing you with the tools to elevate your forex trading game and make more informed decisions in dynamic markets.
Identifying Trend Direction
The primary role of MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) in forex trading is to identify the direction of a forex’s trend. Traders use MACD to understand whether a forex is in an uptrend, downtrend, or if it’s lacking a clear trend altogether.
How to Spot Buy and Sell Signals with MACD
Traders can use MACD to generate buy and sell signals, helping them make informed trading decisions. Here’s how:
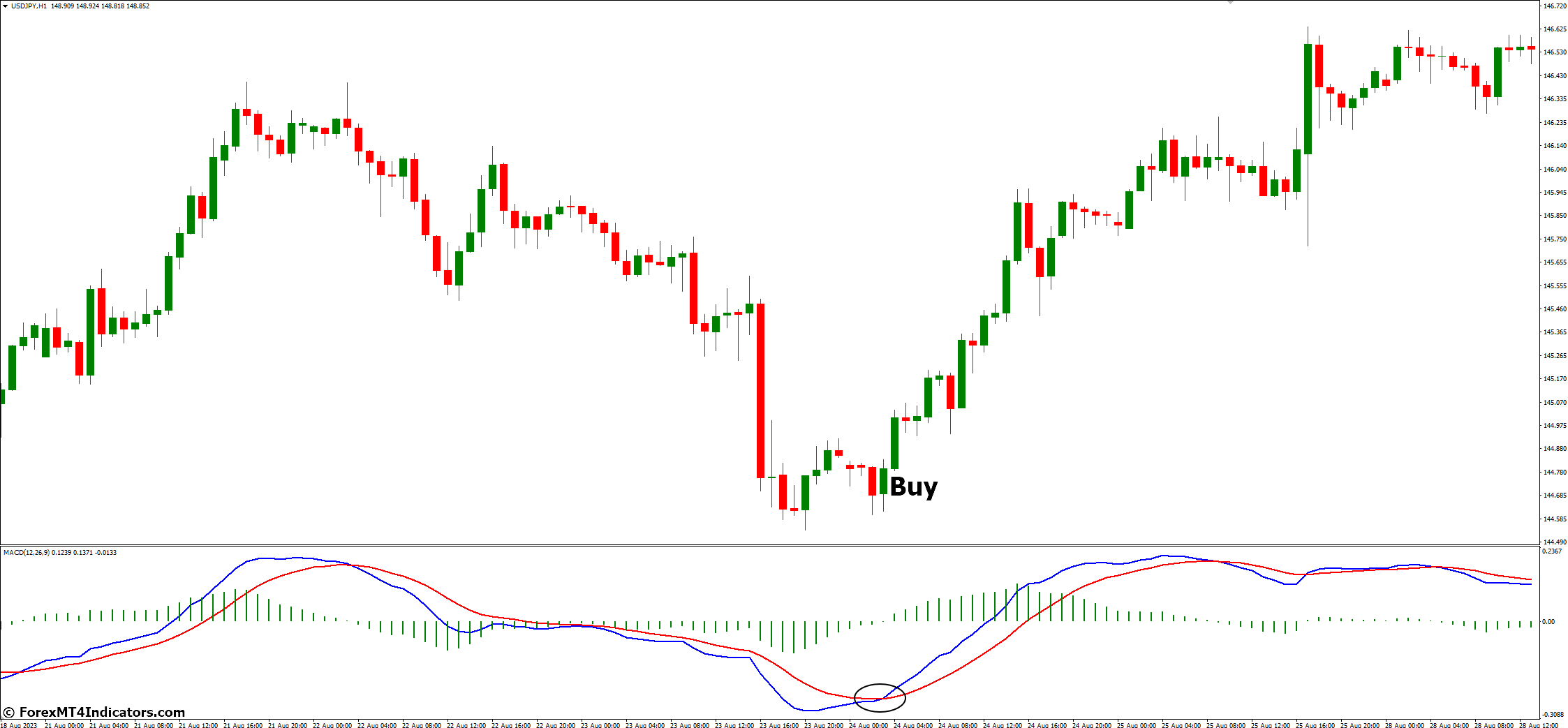
Bullish Signals (Buy):
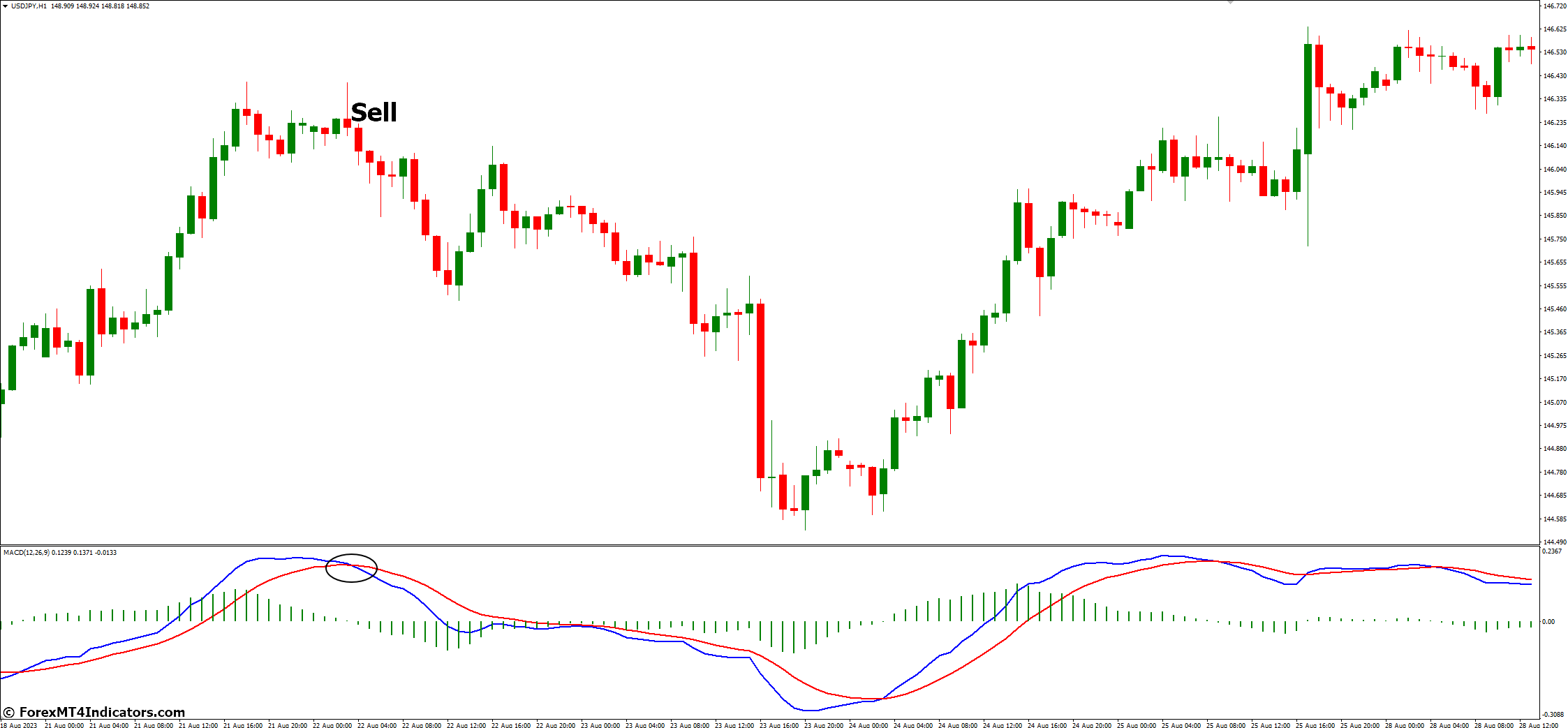
- MACD Line Crosses Above Signal Line: When the MACD line (blue) crosses above the Signal line (orange), it generates a bullish signal. This crossover indicates that short-term momentum is increasing relative strength index to the longer-term momentum.
- Histogram Confirms Bullish Momentum: Positive histogram bars (above the zero line) accompany the MACD line crossing above the Signal line, reinforcing the buy signal.
Example: In the chart, the MACD line crosses above the Signal line, and the histogram bars turn positive, signaling a potential buying opportunity.
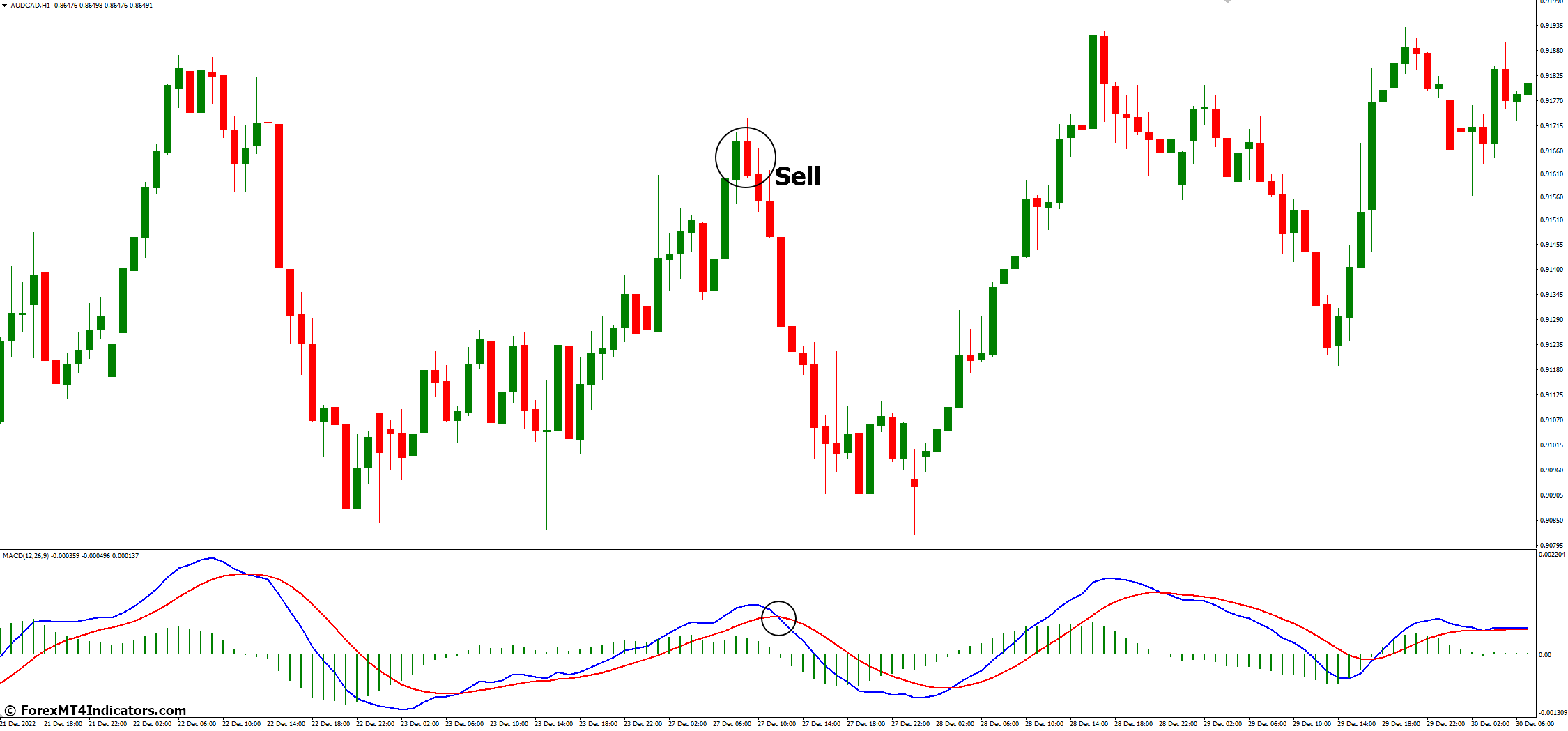
Bearish Signals (Sell):
- MACD Line Crosses Below Signal Line: When the MACD line crosses below the Signal line, it generates a bearish signal. This crossover indicates that short-term momentum is weakening compared to the longer-term momentum.
- Histogram Confirms Bearish Momentum: Negative histogram bars (below the zero line) accompany the MACD line crossing below the Signal line, reinforcing the sell signal.
Example: In the chart, the MACD line crosses below the Signal line, and the histogram bars turn negative, signaling a potential selling opportunity.
Divergence and Convergence (Reversal Signals)
- Traders also use MACD to spot potential trend reversals.
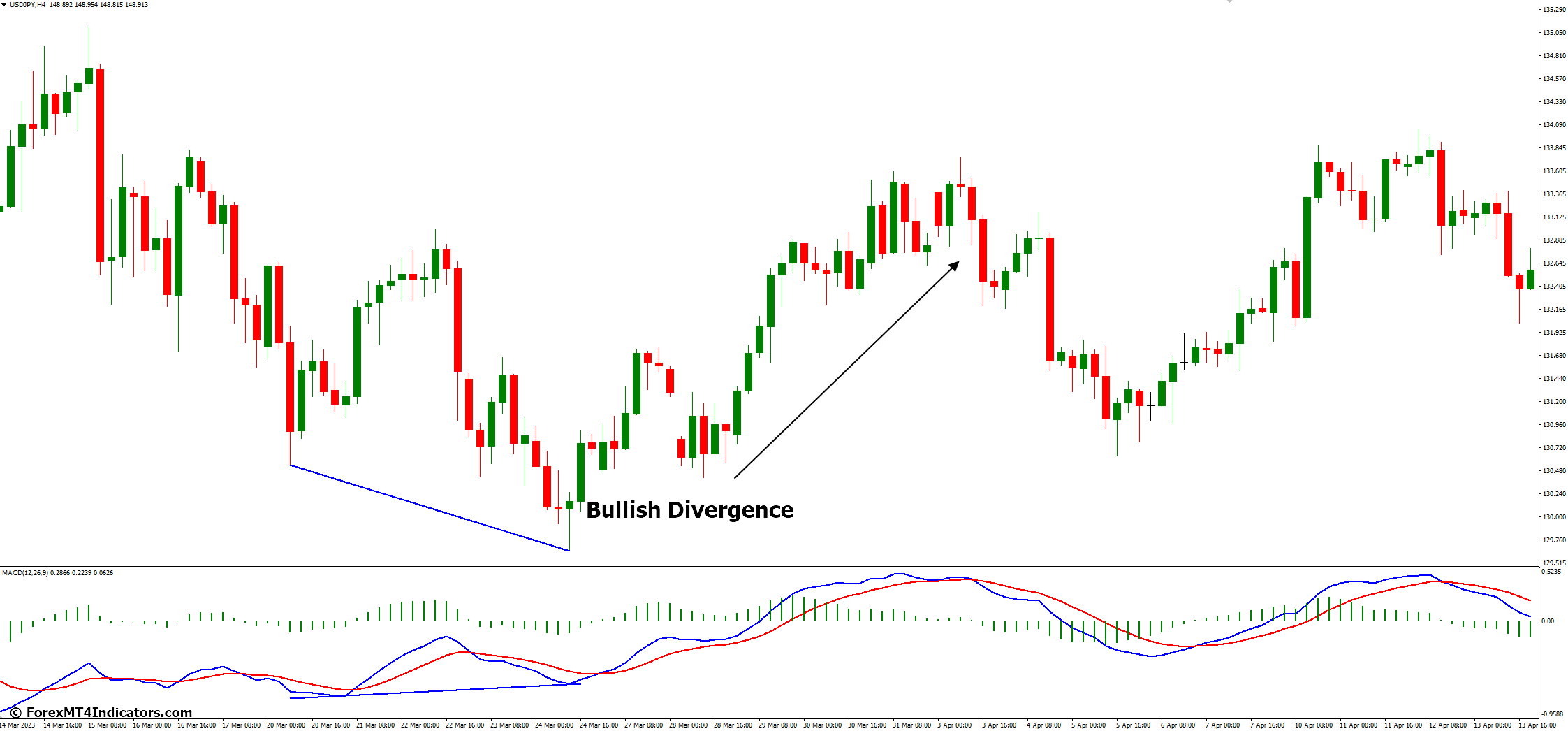
- Bullish Divergence: This occurs when the price makes lower lows, but the MACD histogram forms higher lows. This suggests a weakening downtrend and a possible trend reversal.
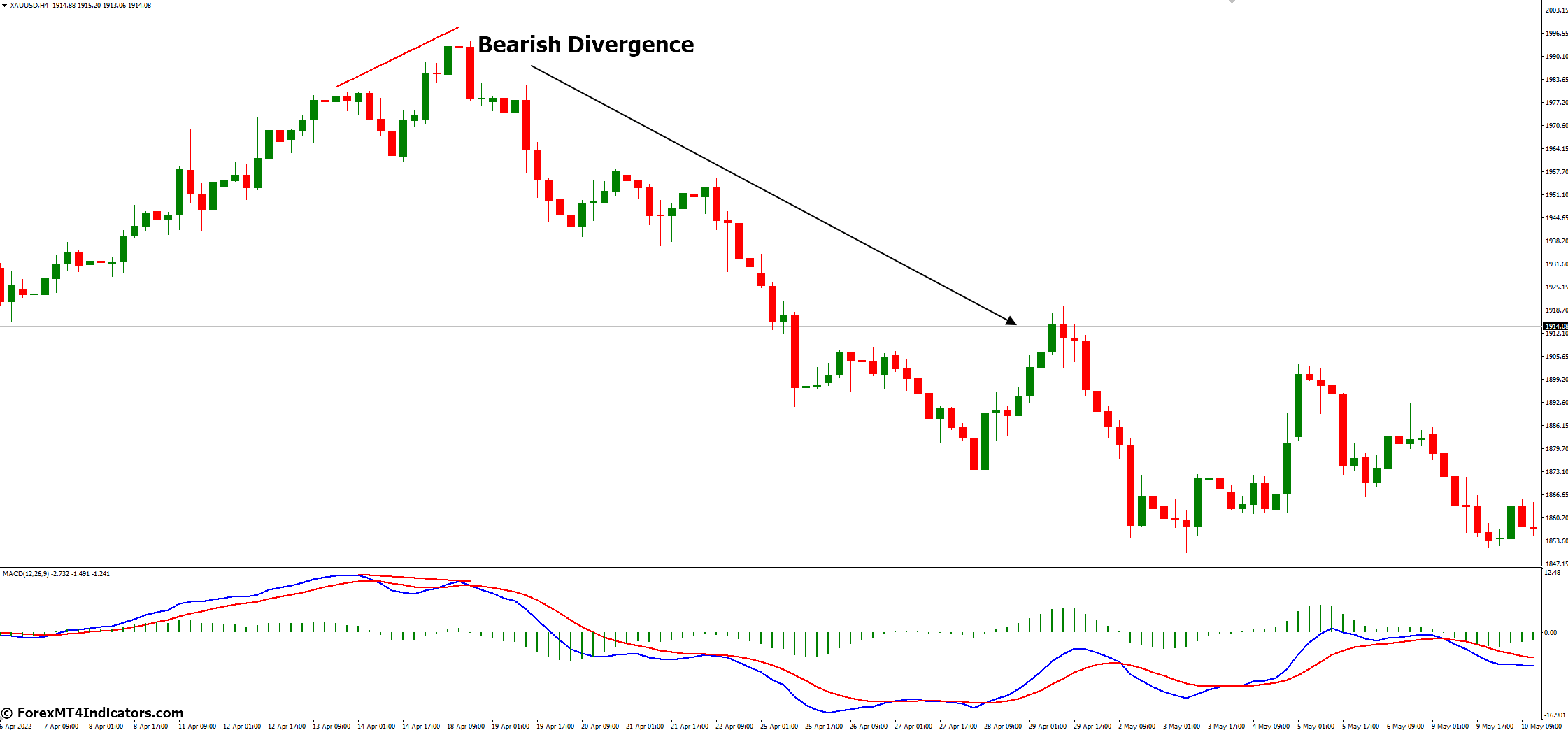
- Bearish Divergence: This bearish divergence occurs when the price makes higher highs, but the MACD histogram forms lower highs. This suggests a weakening uptrend and a potential trend reversal.
Example: In a bullish divergence, the price hits lower lows while the MACD histogram forms higher lows, indicating a potential trend reversal.
The MACD is a versatile tool for traders to identify trend direction and generate buy and sell signals. By paying attention to MACD line crossovers, the histogram, and divergence/convergence patterns, traders can make more informed decisions when trading stocks.
MACD Strategies
Explore effective MACD strategies to enhance your forex trading, from trend identification to spotting trend reversals.
MACD Crossover Strategy
When to Use: The MACD Crossover Strategy is employed to identify trend changes and generate buy or sell signals.
How it Works: Look for crossovers between the MACD line and the Signal line.
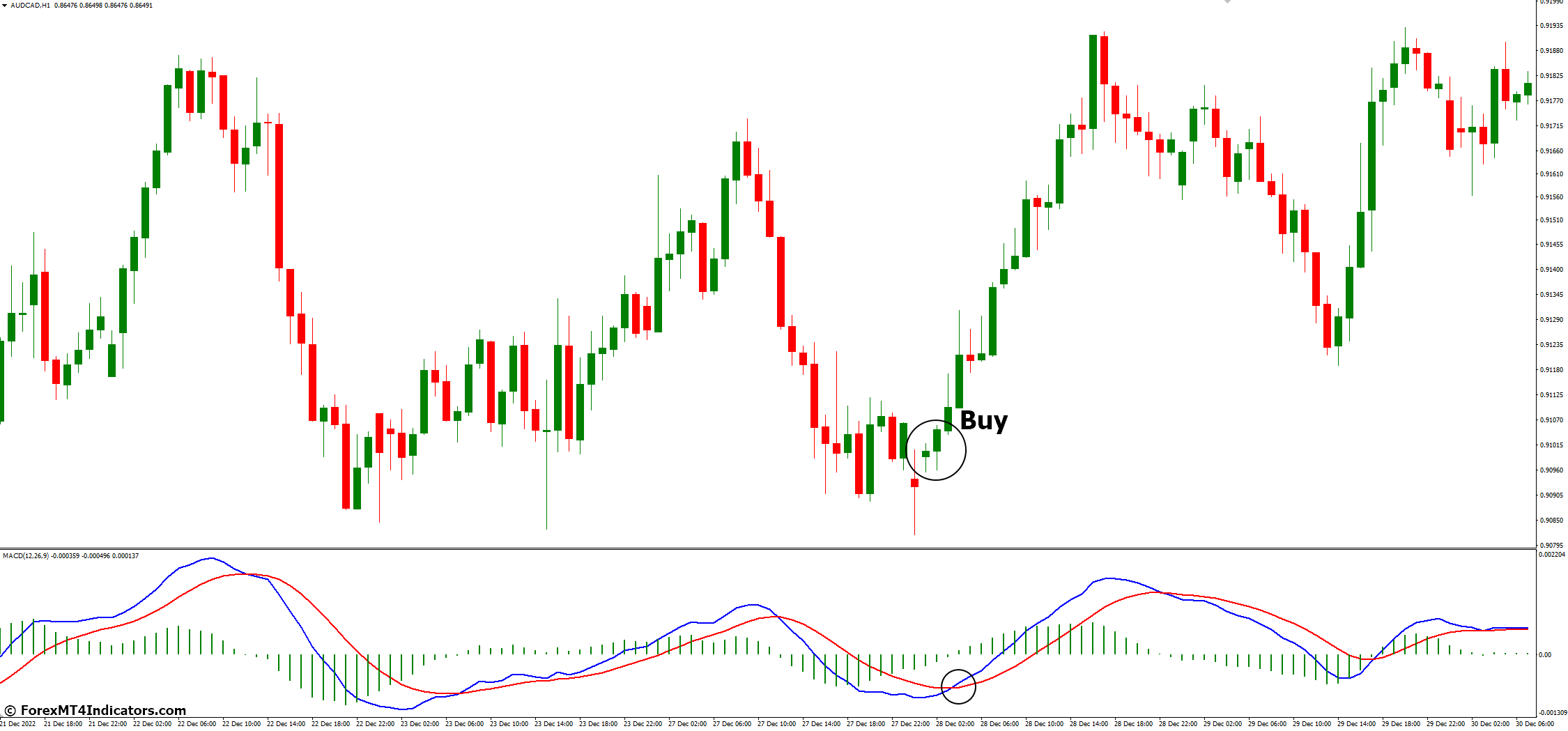
Buy Signal
When the MACD line crosses above the Signal line, it indicates a potential uptrend. Traders may consider buying.
Sell Signal
When the MACD line crosses below the Signal line, it suggests a possible downtrend. Traders may consider selling or shorting.
Example: Imagine a currency pair where the MACD line crosses above the Signal line (bullish crossover), leading to a successful buy trade as the price increases.
MACD Divergence Strategy
When to Use: The MACD Divergence Strategy is employed to spot potential trend reversals by examining divergences between the MACD indicator and the price.
How it Works:
Bullish Divergence
When the price makes lower lows while the MACD histogram forms higher lows, it signals a weakening downtrend and a potential trend reversal to the upside, creating a buying opportunity that is bullish divergences.
Bearish Divergence
When the price makes higher highs while the MACD histogram forms lower highs, it signals a weakening uptrend and a potential trend reversal to the downside, creating a sell opportunity.
Example: In a bearish divergence scenario, the price forms higher highs, but the MACD histogram shows lower highs. Traders may sell or short the currency pair in anticipation of a downtrend.
MACD Histogram Strategy
When to Use: The MACD Histogram Strategy focuses on the histogram’s bars to identify momentum shifts.
How it Works:
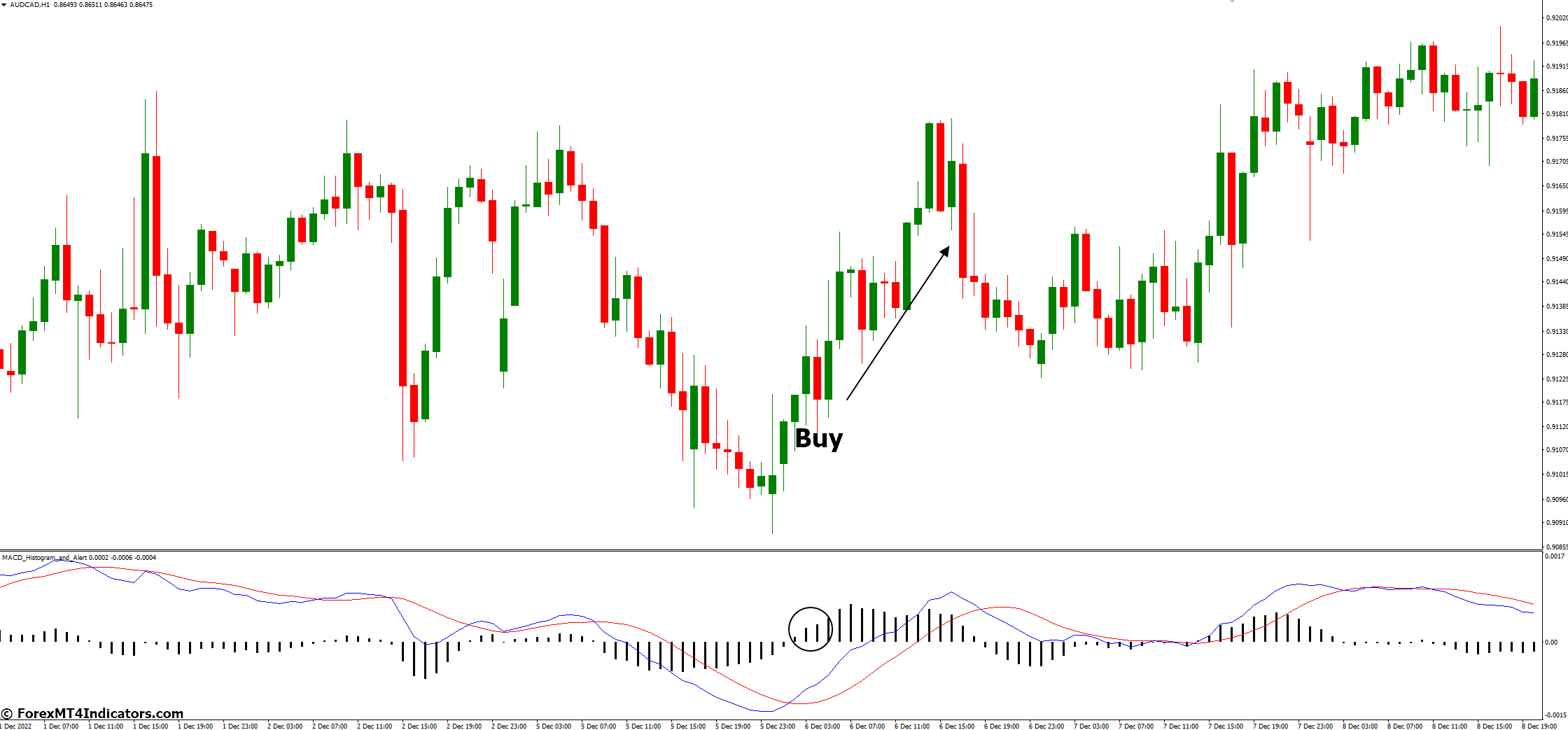
Positive Histogram
Positive bars (above the zero line) indicate bullish momentum, suggesting potential buy opportunities.
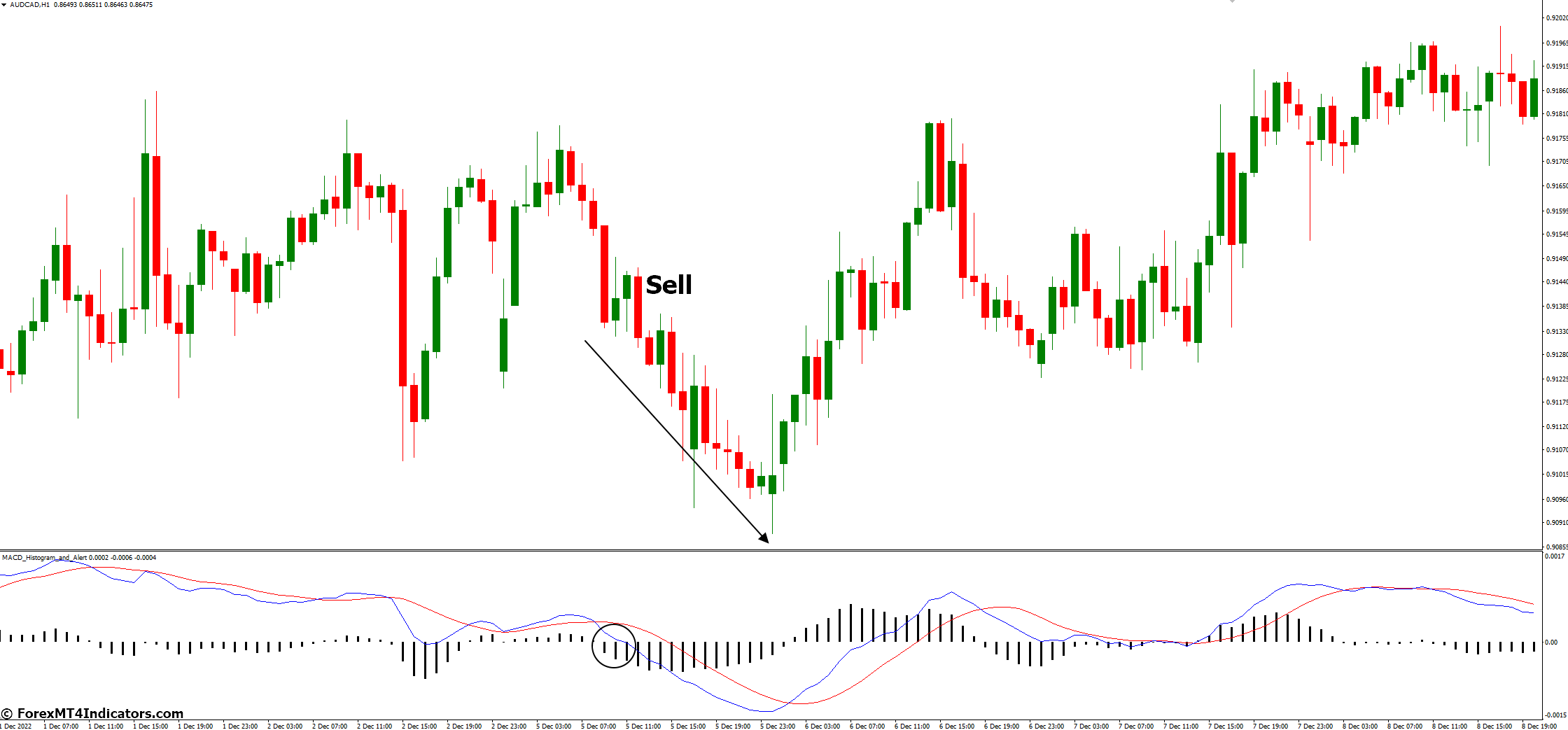
Negative Histogram
Negative bars (below the zero line) indicate bearish momentum, suggesting potential sell opportunities.
Example: When the histogram bars turn positive, confirming the MACD line’s crossover above the Signal line, it strengthens the buy signal. Conversely, negative histogram bars complement a bearish signal.
MACD and Moving Averages Combination Strategy
When to Use: Traders often combine MACD with moving averages to enhance trend-following strategies.
How it Works:
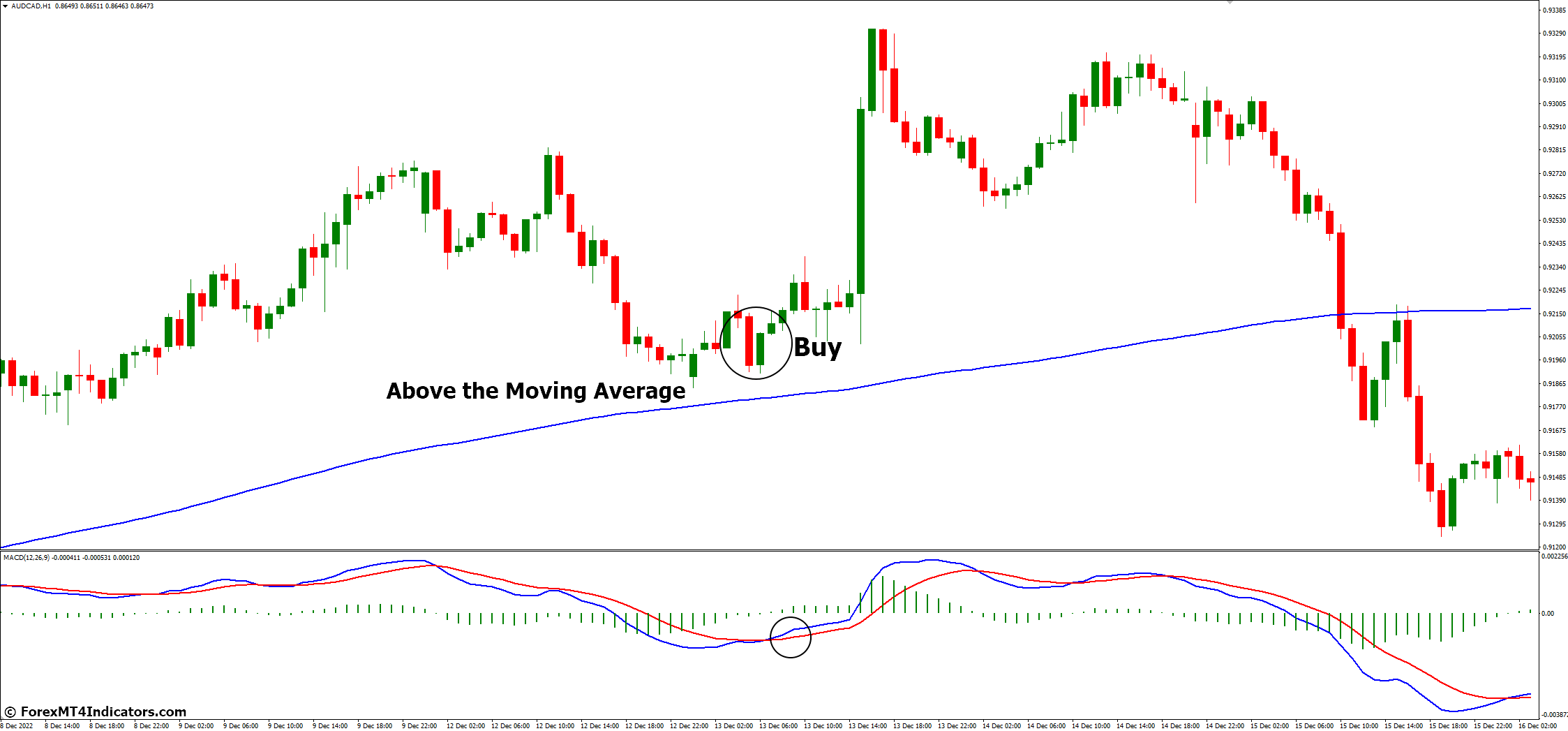
Buy Entry
For an uptrend, the price should be above a longer-term moving average (e.g., 200-day), and the MACD should be in a bullish configuration (MACD line above the Signal line).
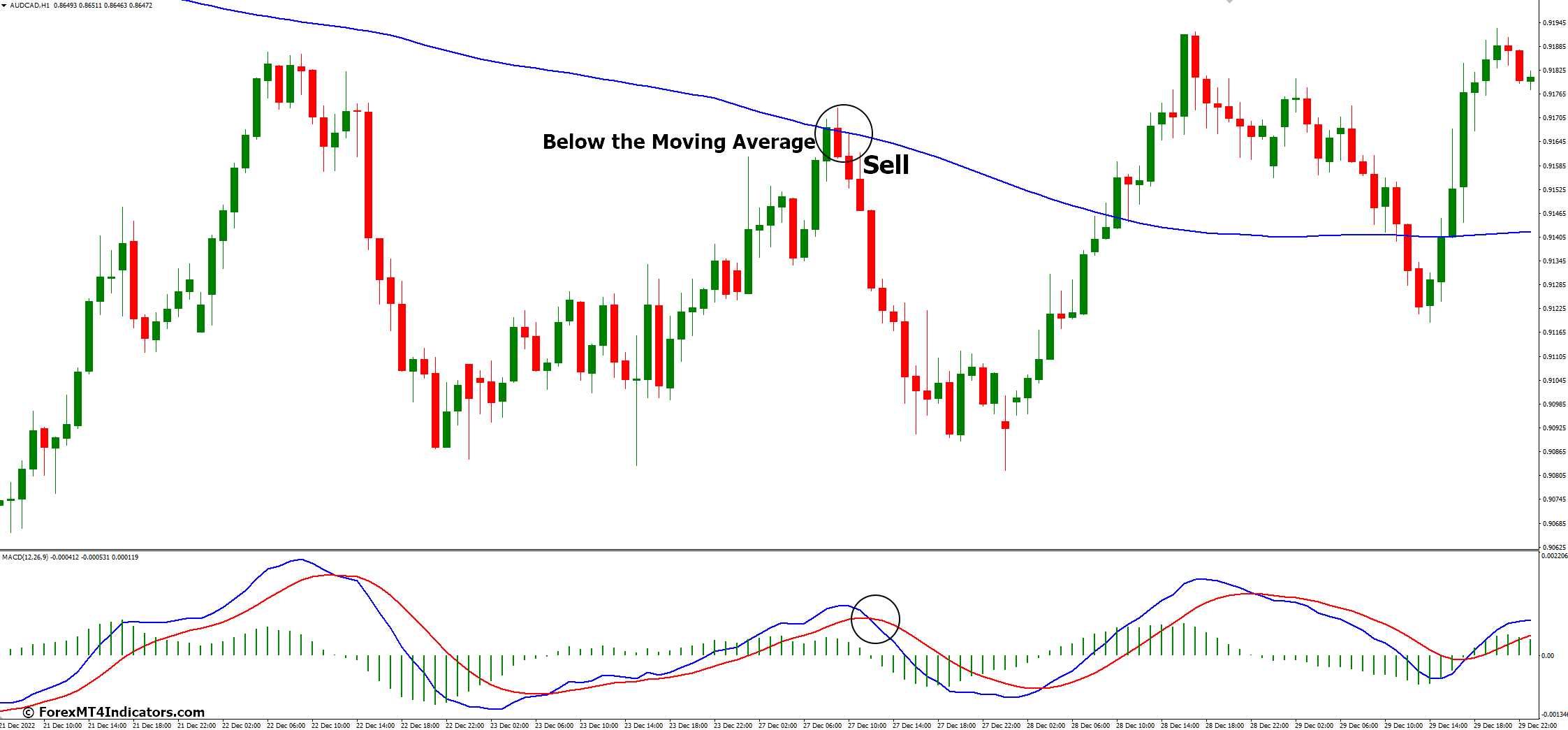
Sell Entry
For a downtrend, the price should be below the longer-term moving average, and the MACD should be in a bearish configuration (MACD line below the Signal line).
Example: In an uptrend, the price is above the 200-day moving average, and the MACD shows a bullish crossover, confirming a potential buy signal.
Successful trades using MACD strategies involve careful consideration of these indicators, market conditions, and risk management.
Remember that no strategy is foolproof, and traders should combine technical analysis with other factors like fundamental analysis and market sentiment for well-informed decisions.
Additionally, backtesting and practice can refine your approach and improve trading outcomes.
MACD Tips And Best Practices
Master the art of MACD with these essential tips and best practices to elevate your forex trading game while minimizing risks.
Use Multiple Timeframes: Examine MACD on multiple timeframes (e.g., daily, weekly) to get a comprehensive view of a forex trend. Longer timeframes help identify broader trends, while shorter ones can pinpoint entry and exit points.
Combine MACD with Other Indicators: To confirm signals and reduce false positives, consider using MACD in conjunction with other technical indicators, such as RSI or support and resistance levels.
Practice Patience: Avoid impulsive decisions based solely on MACD crossovers or divergences. Wait for confirmation from other factors, like price action, volume, and market sentiment.
Implement Risk Management: Set stop-loss orders and determine position sizes based on your risk tolerance. Don’t risk more than you can afford to lose on a single trade.
Backtest Your Strategies: Before trading with real money, practice your MACD strategies on historical data. Backtesting can help you understand how your strategy would have performed in the past.
Stay Informed: Keep up with market news, economic events, and changes in market sentiment. These factors can influence the effectiveness of MACD signals.
Avoid Overtrading: Don’t trade excessively based on every MACD signal. Be selective and focus on high-probability setups to reduce trading costs and minimize risks.
Understand Limitations: Recognize that MACD is not infallible and can produce false signals in choppy or sideways markets. Use it as part of a broader trading toolkit.
Continuous Learning: Stay updated on developments in technical analysis tool and refine your understanding of MACD. Attend webinars, read books, and learn from experienced traders.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring Confirmation: Relying solely on MACD signals without considering other factors can lead to losses. Always confirm signals with additional analysis.
- Chasing Divergences: Not all divergences result in trend reversals. Avoid blindly trading every divergence signal and assess other factors like volume and price patterns.
- Overlooking Market Context: Consider the broader market conditions, news, and earnings reports. MACD signals should align with the overall market trends.
- Neglecting Risk Management: Failing to set stop-loss orders or risking too much on a single trade can lead to substantial losses.
- Using MACD in Isolation: MACD is most effective when combined with other indicators and tools. Using it in isolation may result in poor decision-making.
- Ignoring Market Sentiment: Market sentiment can override technical indicators. Be aware of market sentiment, especially during major news events or earnings reports.
By following these tips and avoiding common mistakes, you can harness the power of MACD effectively in your forex trading endeavors while managing risk and making informed decisions.
FAQ’s
What Does MACD Stand For?
MACD stands for Moving Average Convergence Divergence, a popular technical indicator used in forex trading to analyze trends and generate buy and sell signals.
How Is MACD Calculated?
MACD is calculated by subtracting the 26-period Exponential Moving Averages (EMA) from the 12-period EMA. The result is the MACD line, which represents short-term momentum.
What Are the Key MACD Signals?
The primary MACD signals include crossovers between the MACD line and the Signal line crossover. A MACD line crossing above the Signal line generates a bullish signal, while a crossover below the Signal line generates a bearish signal.
What does it indicate when the MACD line crosses from below to above the signal line?
When the MACD signal line crossovers from below to above the signal line, it indicates a bullish signal, suggesting potential upward momentum in the price trend.
What Is the Significance of MACD Histogram?
The MACD histogram visualizes the difference between the MACD line and the Signal line. Positive bars (above zero) indicate bullish momentum, while negative bars (below zero) suggest bearish momentum. Histogram crossovers signal potential trend changes.
Can MACD Be Used for Different Timeframes?
Yes, MACD can be applied to various timeframes, from daily to weekly charts, depending on your trading goals. Longer timeframes provide a broader view of trends, while shorter ones help with shorter-term trading decisions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering MACD is a crucial step toward successful forex trading. By understanding its components, interpreting signals, and following best practices, you can navigate the markets with greater confidence.
Remember, MACD is a versatile tool that can help you identify trends, reversals, and potential buying or selling opportunities. It’s time to put this knowledge into action. Start incorporating MACD into your trading strategies, practice, and refine your skills.
With dedication and a solid grasp of MACD, you’re well on your way to unlocking your full profit potential in the world of forex trading.